AMD and Intel are two of the most iconic names in PC building, and for good reason. For decades, they’ve been duking it out to offer the fastest, most capable, and most feature-rich processors for gamers, casual web browsers, and professionals alike. The latest models from AMD are the Ryzen 7000 and Intel’s 13th-generation Raptor Lake. These processors offer up to 24 cores, clock speeds that are approaching 6GHz, and more cache than even the fastest CPUs of previous generations could dream of.
AMD’s Ryzen 9 7950X
- 16 cores and 32 threads
- 80MB of cache
- 4.5GHz base clock
- 5.7GHz boost clock
- 170W TDP
Intel’s Core i9-13900K
- 24 cores (8+16),
- 68MB of cache,
- 3GHz base clock,
- up to 5.8GHz boost clock,
- 125W/253W TDP.
Intel’s Core i7-13700K
- 16 cores (8+8),
- 54MB of cache,
- 3.4GHz base clock,
- 5.4GHz boost clock,
- 125W/253W TDP.
Intel’s Core i5-13600K
- 14 cores (6+8),
- 44MB of cache,
- 3.5GHz base clock,
- 5.1GHz boost clock,
- 125W/181W TDP.
While AMD’s processors are generally going to be cheaper than and equivalent to Intel chips, Intel offers overall more powerful chipsets than AMD has available but at a much higher price. As a general rule, AMD’s processors are less expensive and AMD technically holds the record for the fastest gaming CPU with its Ryzen 9 7950X.
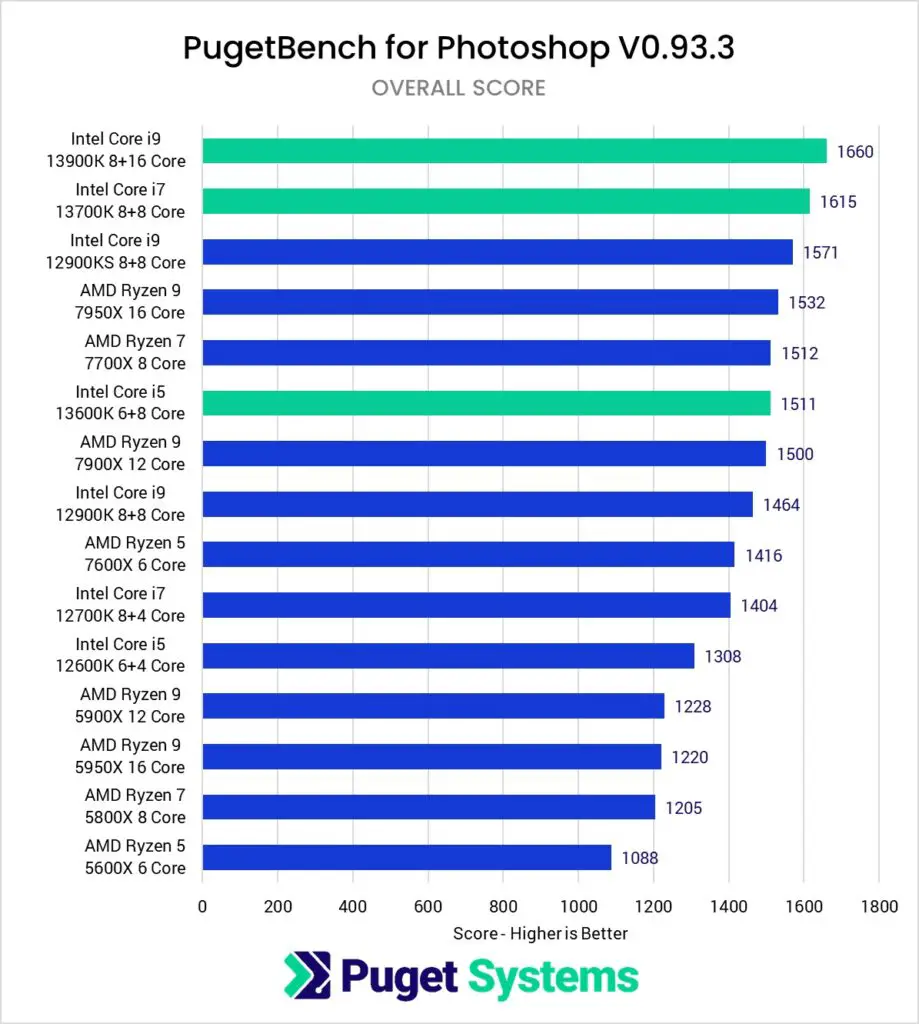
In terms of performance, Intel Core i9-13900K has 24 cores (8+16) and supports up to 32 threads, while the best AMD CPU uses a more traditional 16-core and 32-thread layout. Both chips are neck and neck in demanding games and trade blows in workplace applications. Where more full cores can be leveraged, the 13900K steals the top spot, while applications that rely on more powerful individual cores lean toward AMD. At around the $300 mark, Intel’s Core i5-13600K is also an excellent bang-for-the-buck CPU, offering amazing gaming and productivity performance for a much lower price.
Power Effeciency
In terms of power efficiency, Intel’s processors tend to consume more power than AMD’s, with Intel’s highest-end processors consuming up to 253W TDP while AMD’s top-of-the-line processor consumes only 170W TDP. This means that AMD’s processors are more power efficient than Intel’s, and that Intel’s processors will require more cooling in order to maintain the same performance levels.
Overclocking
In terms of overclocking, both Intel and AMD’s processors support a certain amount of overclocking, but Intel’s processors tend to be better suited for overclocking than AMD’s, given their higher-end clock speeds and fewer cores. Intel’s i9-13900K has the highest single-core clock speed of any processor on the market, and the unlocked multiplier allows for precision overclocking, making it an ideal choice for those looking for the most out of their processors.
AMD or Intel – Conclusion
Overall, both Intel and AMD offer great performance, with Intel offering higher-end performance at higher prices, while AMD offers more mid-range performance at more budget-friendly prices. Depending on your budget, needs, and intended use, you can find a processor that fits your build perfectly.
Get More Tech News Here: hideouthq.com/tech